Varicosity
Varicosity is one of the most widespread diseases of vessels. The blood in veins moves from lower extremities to the lungs and heart.
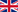
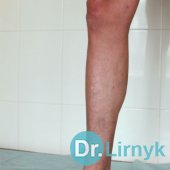
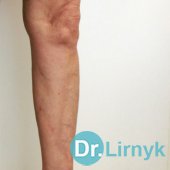
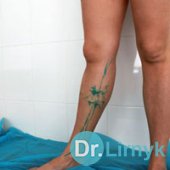
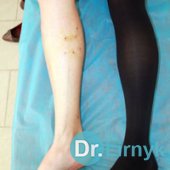
In varicosity veins increase in their diameter, and the wall becomes thinner. Veins become coiled, aneurysms are formed, and insufficiency of vein valves appears. The blood movement towards the heart becomes considerably difficult in varicosity. As a result of this state thrombi are formed, varicosity is transformed into thrombophlebitis and thrombosis. Visually, varicosity of lower extremities is the presence of the dilated and coiled veins on foot, shin and thigh.
In varicosity disease the area of trophic changes of tissues appears in the lower third of the shin up to formation of trophic venous ulcers without healing for years.
Variants of varicosity of lower extremities.
There can be a great variety of variants - from an insignificant capillary net to the enormous vein conglomerates and trophic changes in the skin and ulcers.
- Varicosity of main hypodermic veins and their inflows with the vertical and horizontal retrograde blood current from deep veins into superficial ones.
- Varicosity of inflows of a large hypodermic vein with normal, unchanged main trunks (local varicosity).
- Varicosity of deep veins.
- Reticular varicosity (when there are tiny intradermal veins on thighs and shins).
- Intrapelvic varicosity - it reveals clinically by pains in the pelvis, there is rather often varicosity along the back internal surface of the thighs.
- Varicosity as manifestation of angiodysplasia (vessels development abnormalities).
The clinical picture of varicosity
One of the first complaints is that varicosity is a cosmetic defect.
Complaints can be absent at the stage of compensation of the venous blood circulation.
While the disease is progressing, fatigability, the sense of heaviness in feet, convulsions in gastrocnemic muscles, especially in the evening, and sometimes and at night, as well as paresthesias appear. Edemas appear in the evening, especially after the long standing, but after the night rest they disappear completely. Then if the treatment is absent, edemas do not disappear after the night rest. In the course of time along with varicosity progression and decompensation of the bloodstream, such trophic disorders as induration, pigmentation, dermatitis, lipodystrophy, dermasclerosis, and then trophic ulcer appear. They are more often localized on the internal surface of the lower third of the shin.
The treatment of varicosity
The purpose of treatment is renewal of the blood circulation in the damaged extremity.
There is a great number of approaches to treatment of varicosity, however, at present venectomy is the most effective method of treatment.
Lately the minimally invasive methods of the operative treatment are shown to advantage, they are carried out through the microscopic cuts of skin or through the punctures of the skin (minivenectomy, miniphlebectomy, short stripping); however, they require the presence of the special tool and special training of surgeons.
Laser coagulation of veins is the method planned as an ambulatory operation. The vein is not removed, and the intravenous obliteration of the vein is made (simpler speaking, the vein is burned by a high power intravenous laser). The advantage is that the operation is possible through punctures in the skin. It gives a good cosmetic result. The disadvantage is that it is possible only in the "linear" veins changed by varicosis. When veins are strongly coiled, it is rather difficult to pass a laser emitter along the whole vein and it is not always possible.
Operations with the application of endoscopic tools (operation endoscopes). These operations are used when it is impossible to conduct the cut of the skin in the vein's projection. These are the cases when a perforating vein is under a trophic ulcer.
In some cases the application of sclerotherapy is possible more frequently as the auxiliary method (simpler speaking, a vein is burnt by the special chemical compositions). But lately it is used less, foam-form sclerotherapy is preferable. It is not used frequently by vascular surgeons because of a great number recurrences.
Medicinal therapy is required as auxiliary and independent method at different stages of varicosity in the presence of contraindications to operative treatment, and in post-operative therapy.
Compression therapy is needed at all stages of varicosity. When using the compression graduated knitted wear it is possible to stop disease progression and even remove some clinical symptoms.
Treatment of varicosity should be complex and individual, and includes conservative and, if necessary, operative treatment.
Treatment must be conducted by a doctor, a vascular surgeon, who after diagnosing the patient's vascular system determines the therapeutic scheme taking into account the peculiarities of the individual patient.